
Chapter 5 – International SEO – A guide for you to rank internationally and increase revenue
Photo from marketyourbiz.agency
Originally Posted On: Chapter 5 – International SEO – A guide for you to rank internationally and increase revenue – Market Your Biz
Chapter 6 – International SEO
What Is International SEO?
In the previous chapter, you learned about local SEO and how it can uniquely benefit businesses whose potential customers are located within a certain vicinity or area. In this chapter, we shift our focus to international SEO. But wait, what does international SEO mean?
International SEO refers to the optimization process that helps Google or any other search engine recognize the countries you want to target through your business. It also helps the search engines identify the languages you utilize for your business. While local SEO might target certain neighbourhoods or even cities, international SEO is generally directed towards websites that wish to cover a much larger geographical scope such as certain countries or regions around the world.
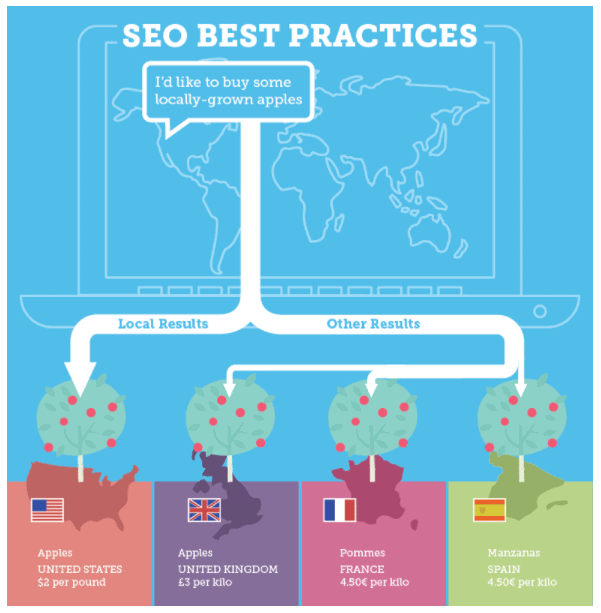
Why Does Your Website Need To Go International?
If your business website deals with international visitors, you must optimize your website to anticipate the needs of the different audiences that you are targeting. For example, a company selling its products in both the United States and Spain will probably have significant differences in the way it presents itself depending on the location of the visitor. An American visitor may view the website in English while someone from Spain may see a version of the same website written in Spanish.
What elements for international visitors must you focus on? Language is just one of the many components that can be adjusted to make international SEO work for you.
If your website caters to different countries or regions around the world and you have decided that international SEO is for you, here are a few general guidelines to look into:
- Your website must state the countries you want to target (also known as country targeting). This requires URLs that are internationally friendly which entails adding country codes in your URL, e.g., “us” for the United States, “jp” for Japan, “uk” for the United Kingdom, etc.
- Your website must state the languages you want to target (also known as language targeting).
- You must remember to generate content using the targeted language as it not only helps you in your ranking, but also helps with user engagement.
Some websites deal with a particular country or a language. If you plan on something similar, your targeting goals are less. E.g., if you have an online book publishing company specifically for the Spanish language, Spain is not the only country for its sales. Hence, your target must be the language and not the region.
After outlining for you the three basic requirements for launching a website that employs international SEO, let us now move on to a more thorough checklist of considerations for you to use.
International SEO Checklist:
You can refer to this checklist to see where you rank on the international SEO process. Don’t worry if you don’t understand every item on this list. We will discuss them further in the section that follows.
Research Section – Check Your International SEO Potential
To determine if your website can develop a presence, look into your:
- Current website traffic
- From other countries
- From other languages
- Recent organic search visibility
- Keyword results in the shortlisted countries and languages
If your SEO meets the criteria in the Research Section, proceed to the next checklist.
Targeting Section – Target Your International Web Visitors
- What to target
- Country / language targeting
- Behavioral patterns / characteristics of international visitors
- International competitors
Once the first two sections are complete (i.e., Research Section and Targeting Section), you’re ready to move on to the next steps.
Optimize Section – Develop an Internationally Targeted Site
- Choose a web structure
- Localize your website
- Navigation through your chosen web structure
- Hreflang/ Canonical tags
- Promotion within international community
- Geolocation
- Local IP address
After finishing the Optimize Section, proceed to measure your progress.
Measure Your International SEO Process
- Did you track each web version independently?
- Did you perform a follow-up with international search visibility?
This checklist answers your questions regarding your international SEO process. Now let us see the fundamentals (Research, Target, and Optimize) in detail.
The Fundamentals of the International SEO Process
You must know the fundamental elements of the international SEO process. They help you prepare your plan of action.
There are three primary phases to begin your international SEO process: research, targeting, and optimization. Let’s get started.
Research
The international SEO process requires extensive research in the beginning. This research helps you identify areas you need to work on for complete optimization.
Before we begin, ask yourself: What is the status of your current international organic search?
To answer the above question, you need the answers from our Research Section – Check Your International SEO Potential.
To learn more about your website traffic, search visibility, and keyword results in your chosen countries and/or languages, you can use the Google Analytics Tool. Refer to Geo reports which is below the Audience section.
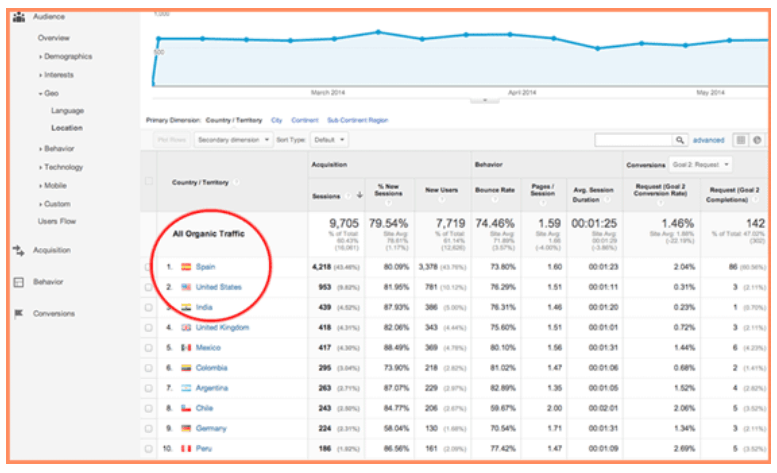
You can also utilize Google Webmaster Tools to filter by location.
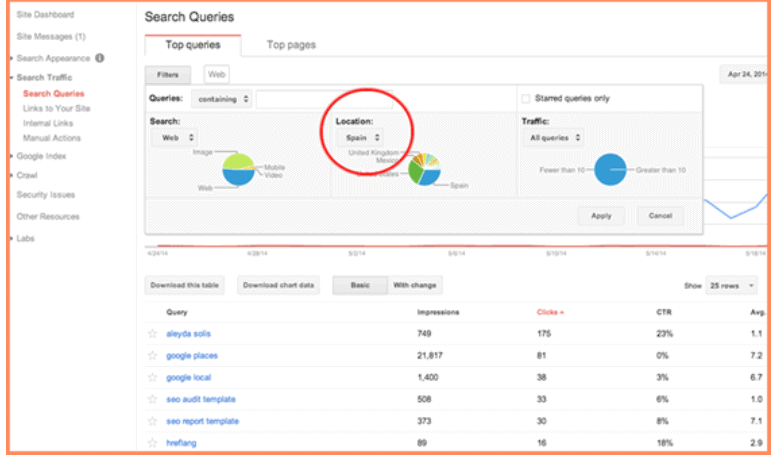
Finding the answers to these questions helps you formulate your strategy for international SEO optimization. If you know what countries and languages provide you traffic, you can customize your site to give international visitors from the same country or who speak the same language content based on their local behaviors, preferences, and culture.
When you perform this research, you might find out that your website already receives a reasonable amount of organic traffic. You can then focus on the existing traffic you have based on country or language for the optimization process.
If, however, your organic search traffic is low, you must find other international markets for your SEO process. This will entail more resources from you as you begin your international SEO efforts.
The next question you must ask yourself is: How much potential does your international organic search entail?
It is assessment time! Evaluate the potential of your targeted countries and languages of your website to answer the above question.
You require keyword research to fulfill this step.
- Find out what the relevant keywords and phrases are from your international visitors. These queries should be related to your business, products, or services you provide.
- What is the organic search volume for these keywords and phrases per country?
- How competitive are the keywords per country?
- What current rank do you hold for these keywords in the targeted markets?
The keywords that are already bringing organic traffic to your website can help you find other relevant keywords. How? By using tools like Ubersuggest, an SEO and keyword discovery tool. We recommend this tool because of how simple it is to use. You only have to enter your keyword in the search bar to receive a list of keyword ideas.
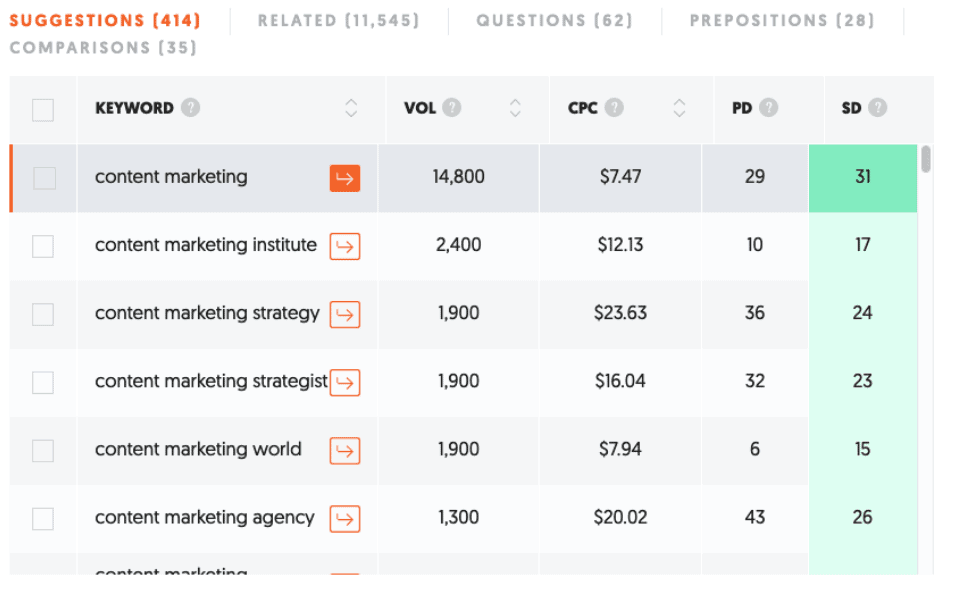
In addition to providing you with related keywords, Ubersuggest also gives you relevant information surrounding the existing competition for the keywords you are considering. It gives you information about keyword difficulty (how hard it is to rank in Google), cost per click (CPC), and paid difficulty (the level of difficulty you’ll have to face if you were to run a campaign with that keyword).
Once you have all this information, you must find out how your web pages rank by country.
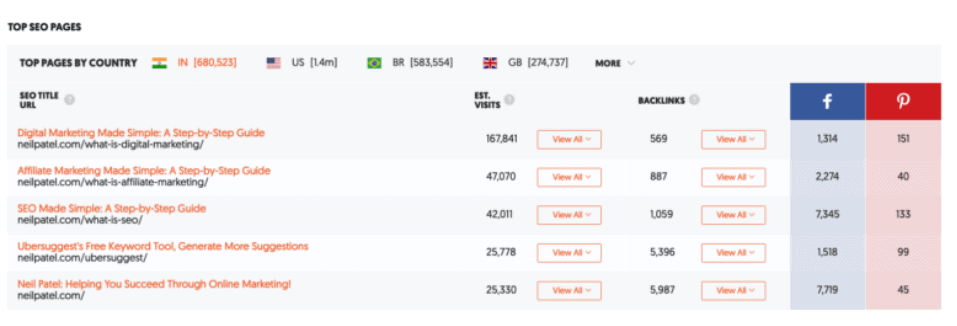
For the optimization, you need native language support. It is necessary for keyword research.
When you use Google Translate, it is not always accurate. Words and sentences can have different contexts, and the literal translation may change their meaning. Similarly, if you want to use Google’s Market Finder for easy translation, it may mislead you. Occasional usage is not entirely wrong, but it should be relevant.
Once you complete the steps of finding the relevant keywords and finding out their organic search volume, it is time for you to establish the ranking difficulty for each keyword.
Moz Keyword Explorer is beneficial in terms of finding the competitive level of the keywords. There are other tools like Authority Labs or Unamo SEO that work as rank checkers.
By now, your research is complete. Let’s proceed to the next step: targeting.
Targeting
Your priority should be targeting countries based on their ability to generate organic search traffic for your website using relevant keywords.
If targeting a country is not yielding results, you can always target a specific language.
You must ask yourself: What would yield better results, targeting countries or certain languages? Only you can determine the answer as it depends on your company’s core nature. For example, companies like Walmart need to target the United States because of where their physical stores are. On the other hand, software companies like Atlassian, the developer behind an English project management software, needs to target all English language users.
This process maximizes your chances of receiving organic traffic and desired conversion rate. Once you achieve that, you can gain relevant visitors to your website based on your targeted audience.
There are different types of structures depending on the characteristics and restraints of your website.
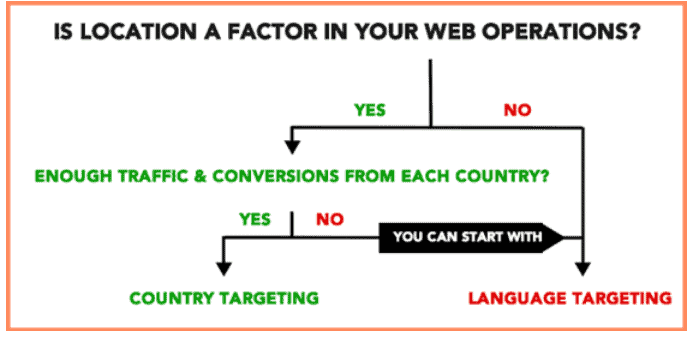
Below is an overview of the different ways you might decide to target specific countries or languages.
Country Targeting
Chances are, you’ve probably already experienced (and can probably already guess) how specific countries are targeted by different websites. You may have noticed that websites in your country have a common two-letter code. This is how webmasters use URLs to target different countries. There are, however, a few different ways to integrate them into URLs. They each affect how your website is structured and comes its own drawbacks and benefits:
- Country Code Top-Level Domain (ccTLDs)
This structure for country targeting is beneficial as it provides a specific country extension, but it requires more effort to increase the domain’s popularity as it starts out as new and independent. This is ideal for large multinational companies who have the resources to acquire a domain and build it up from scratch.
Example: https://comprehensiveseoguide.us
Google treats some ccTLDs as generic top-level domains (gTLDs) which are not associated with any country code. A generic top-level domain refers to the kind of website. For example, websites with “.org” in their URLs generally refer to nonprofit organizations, website URLs with “.info” are generally used for information-driven websites, etc.
ccTLD is a desirable web structure, and companies like Tripadvisor and Amazon use it.
- Subdomains
Subdomains are a great option if you have gTLD, but do not want a complicated structure. When you need to index a large amount of content, you must separate different web versions into sub-directories.
Example: https://us.comprehensiveseoguide.com
On the down side, Google recognizes each URL as a different domain and you will need to build up SEO for each. Though it is much less complicated in structure, this option entails a lot of effort in increasing every individual subdomains’ popularity.
Companies like Shop and Beats by Dre use this structure for country targeting.
- Sub-Directories
You can get profitable results if you use this structure along with gTLD. In terms of implementation, this is the easiest as it is just another folder on your site. You also have the advantage of inheriting all the ranking from your root domain
Example: https://comprehensiveseoguide.com/us
Companies like Spotify and Electronic Arts use this structure for country targeting.
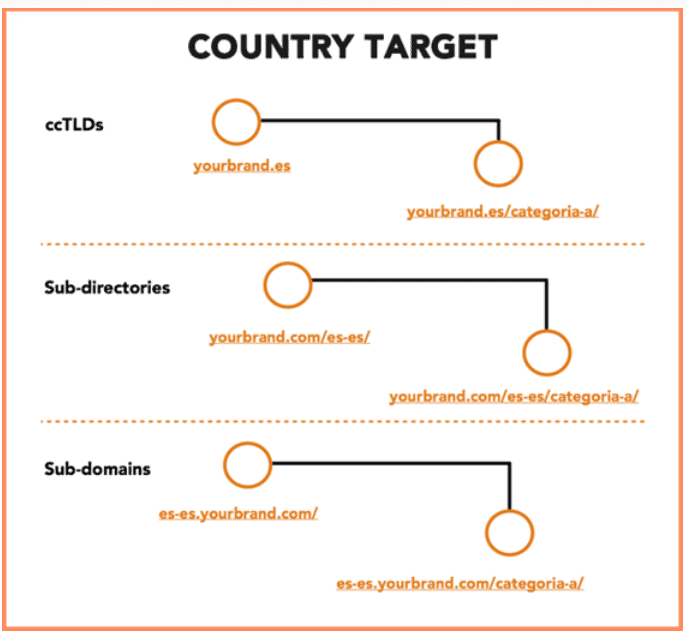
Language Targeting
Language targeting relies on Google’s machine learning algorithm to detect the language/s a user knows. Similar to country targeting, it makes use of the URL structure to integrate language codes that determine the language in which a web page should be displayed.
The structure you choose to implement for language targeting is, in principle, the same as the one we just covered for country targeting. Different language websites separated by subdomains are interpreted by Google as individual domains for which you will need to build up optimization from scratch. Subdirectories, in contrast, will share the same SEO equity as your root site.
- Language targeting by subdirectories are used by companies like Skype and Atlassian. URLs that employ this structure typically look like this: https://www.comprehensiveseoguide.com/en
- Language targeting by subdomains are used by companies like Wix and WordPress. Sites that employ this method have URLs like this: https://www.en.comprehensiveseoguide.com
When you select one of the alternatives as your website structure, make sure you are consistent in the structure you choose. Overlapping these alternatives will result in complications.
Once you finish research and choose your targeting structure, it is time to optimize.
Optimization
Optimization is fundamental as it makes your website crawlable, indexable, and relevant. It also helps in sending out properly targeted signals to avoid any issues with search results.
Let us look at some general international web optimization elements:
- Crawlable and Indexable
Different web versions need to be crawlable and indexable. It requires independent URLs following the relevant web structure you choose. It is not wise to use scripts or cookies as they make indexing difficult for search engines. If you are using different web versions, make sure that they are linked together.
If you have many web versions, you can only link the main page to the most popular one and you should feature all the web versions on one internal page.
- Relevance
Translation or localization (by language or country respectively) of different components is crucial for every international web version. You can do it using the keywords and phrases you acquired in the research. The elements you can work on are:
URLs, Title and Meta Descriptions, Menu and Navigations, Headings, Images and Alt Descriptions, Core Content, Reviews, among others.
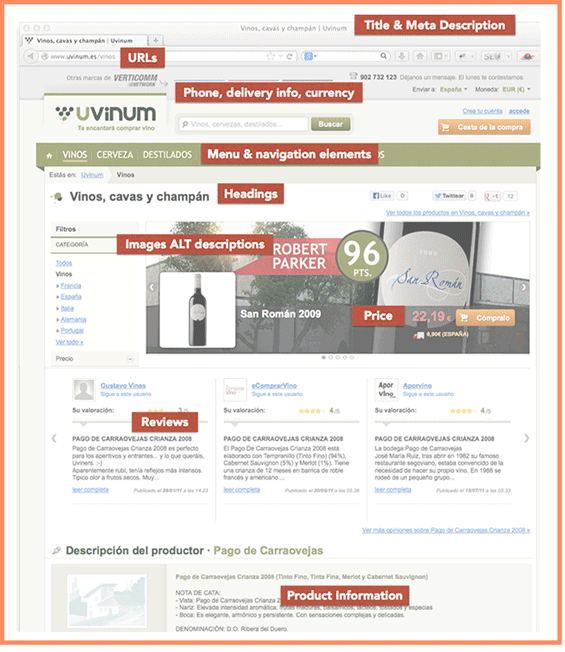
Some websites have titles and URLs in English, but other elements of the page are in another language. This inconsistency confuses users and makes your page irrelevant to search engines.
Your international visitors might have questions about your content. It is a good practice to answer them when translating other components. This practice increases the credibility of your website.
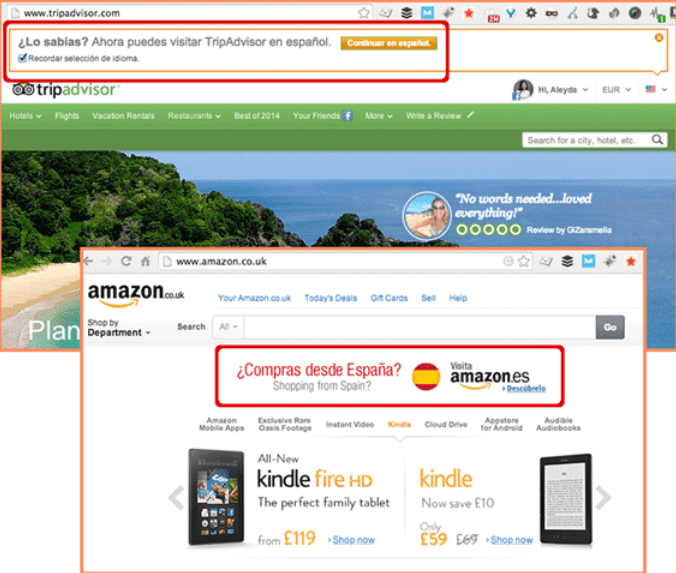
- Automatic Detection of Language or Country:
If you want to know the country from where your international user is visiting your website, you can check their IP address. If you want to know their language, there are options available on the browser. You can conduct this research to redirect the users to the correct web version.
When looking to introduce language or geographic customizations:
- Make sure not to use pop-ups to learn more about your audience as they can be too obtrusive.
- Be careful when asking for information from visitors or making suggestions in your site. Visitors may not always understand the context of your questions or may feel intruded upon by sudden and unwarranted suggestions.
- Ensure that all your web versions are crawlable.
- Specify Language:
You need to display the character encoding of your page, specifically when you handle non-ASCII characters. ASCII characters stand for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. It refers to the characters you can find on a traditional English keyboard (Alphabets A-Z, Numbers 0-9, and punctuations). Non-ASCII characters are characters that are not in the English language.
You can specify the language in which your web page should be displayed in several ways:
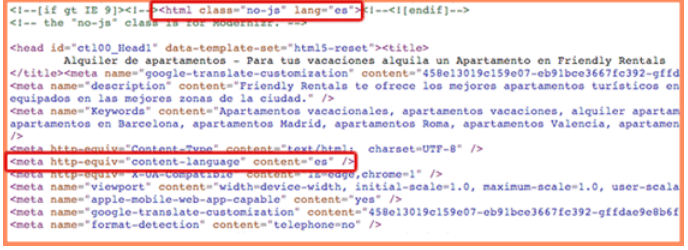
- HTML Lang, Content-Language Meta Tags, and HTTP Headers
HTML language attributes and meta-tags are ways to identify language by search engines like Bing. You must set the right annotation within the html tag and add the correct language code.
Google does not utilize these attributes as it depends on its own algorithm in matching different target audiences with different versions of a website.
- Language Specification by Hreflang
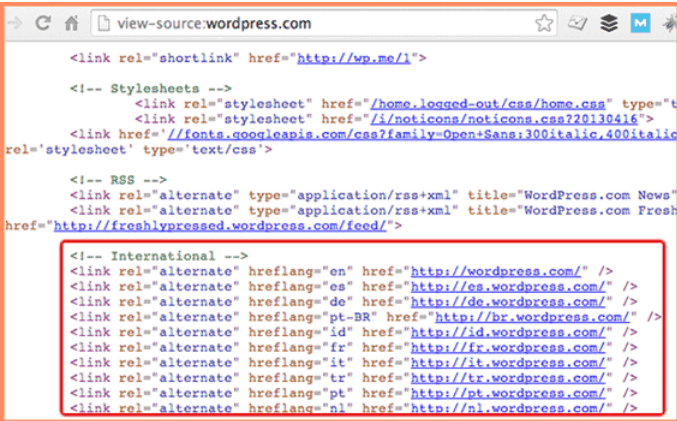
Hreflang annotations are essential for search engines like Google. They identify the language used in your webpages and enable Google to serve that language version to users who are performing a search in that same language. Here are some things to remember about the hreflang attribute:
- The simplest way to use hreflang is by including it as an HTML link in each page header.
- Specify it as an HTTP header for non-HTML files.
- If there are many web versions, you can add them in the XML sitemaps. (An XML Sitemap refers to a file that contains the list of URLs for a website)
You can use Hreflang with canonical tags. Canonical tags tell search engines which URL is the official version of a page.
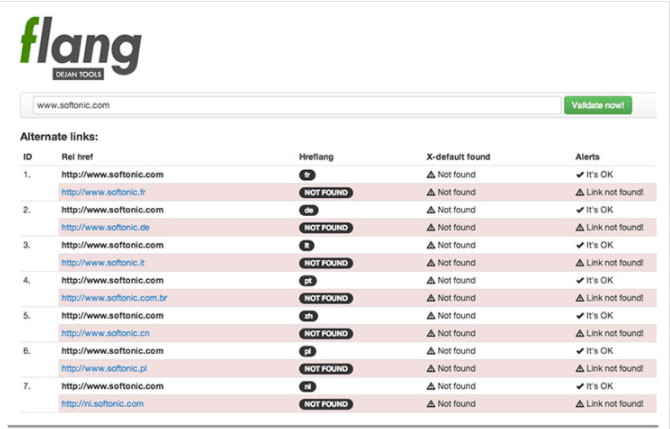
There are tools like flang that work as a validator for the implemented annotations. You can also use SEO crawler tools like Rob Hammond to check many pages at once.
- Geolocation
If your plan includes targeting countries, you need to geo target your international web versions apart from specifying the language. To do this, you can use:
- Country Specification by Hreflang
Hreflang is not only useful for specifying the language version that search engines should serve to specific users, but is also useful in targeting specific countries. Hreflang gives you the ability to target people speaking a certain language in certain countries.
For example, the English language is used the world over, but by using the hreflang tag, you can target English speakers in the United States and the UK. There are also instances when you may be targeting English speakers, but would like to serve English speakers in the United States a different version of your web page than English speakers in the UK. Tweaking your hreflang attribute allows you to do either of these things.
In writing out your hreflang instructions, remember to include language codes as adding only country codes will not work.
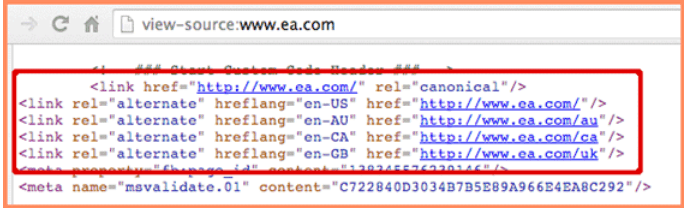
- Geolocation through Webmaster Tools
Webmaster tools are particularly useful for websites that utilize sub-directories or subdomains in their website structure.
However, this is not the case for websites utilizing a country code top-level domain (ccTLD) structure. For ccTLDs, use instead the Google Webmaster Tools, Bing Webmaster Tools, or Yandex Webmaster Tools.
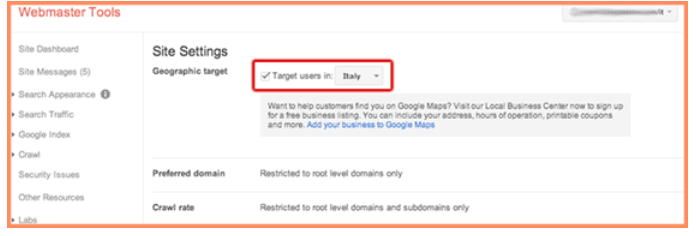
- Your hosting location
Maintaining a static IP location for your website used to be important for reasons of stability and simplicity. Websites with a static location were easier to find and more compatible with different operating systems. Times have changed, however, as search engines can now get more accurate geolocation signals by using ccTLDs or webmaster tools.
Now that you have a clear idea of the fundamentals of international SEO, let’s take a deeper look at how international SEO is different from regular SEO.
How Is International SEO Different from Regular SEO?
If your home country’s website is similar to the international web version of your website, it will not attract traffic. You need to localize the international web version to match the targeted country’s local audience to help improve user experience and make your international version more crawlable.
The fundamental difference between regular SEO and international SEO is regular SEO does not involve unique approaches or web versions for different countries. That is what changes in the international SEO process. Regular SEO focuses on a broader means of ranking, but an in-depth international SEO process focuses more on details like country and language targeting. International SEO is also more focused on helping a website rank in the targeted country using the appropriate web version of the website.
Let’s delve into the advantages of a multilingual website.
How Does a Multilingual Website Help?
If you want your international web versions to rank, you need to work on growing its multilingual features. Google tries to personalize user experience as much as it can, and in doing so, it not only answers queries based on your location but also your language.
There are websites like Kinsta who saw an 18 percent boost in organic traffic by translating their content into ten different languages.
Another reason why a multilingual website helps is it offers a better user experience. Your efforts in the multilingual website help your conversion rates.
But what do you prioritize in building a multilingual website? The answer is international keyword research. Let’s look at the steps involved.
International Keyword Research
By now, you know why a multilingual website helps your international SEO process.
It is important to note, however, that you need professional translators because they understand the culture and the background of the targeted language. Once you are clear about this, there are several steps to perform international keyword research:
Keywords List
You know how to do this step from the research part of the fundamentals of international SEO. Hence, keep this list of keywords ready.
Translation
It is time for you to translate these keywords into your targeted language. As a bonus, try translating all the relevant keywords and phrases which you believe are related to the original keywords.
Analyze
To maximize your efforts, try analyzing your keywords. As mentioned above, you can use Ubersuggest for analyzing which keywords will be beneficial for you.
There might be several keywords that may generate organic traffic, but do not help with conversion. Analyze them to avoid wasting your efforts on useless keywords.
Competitor’s Focus
Once you have your keyword list, you need to know what keywords your competitors are using to generate organic traffic for their sites.
Tools like SEMrush’s Domain VS Domain help you identify these keywords. Before you use these keywords, remember to analyze them.
Organizing Your Content
It is time to optimize your content. You have your keywords list, and now you need to use them in a proper context. This is where you employ professional translators to help you deal with other languages.
Track Your Keyword Success
Once you make your web version public with your keywords, you must track how each keyword performs. This step helps you to further the optimization process.
Now let us move on to the targeting signals you can use for international SEO.
What Are the Technical Signals for International SEO?
Technical signals help your website become more crawlable and indexable. The more technical signals you send, the easier it becomes for search engines to identify your targeted countries and languages.
Hreflang Tags
We mentioned hreflang tags before in the optimized part of the fundamentals of international SEO. To refresh your memory, an Hreflang tag works by optimizing your URL to help specify the language you want to target. By now, you also know that tools like flang Hreflang can help you generate these tags.
X Default Tag
xDefault tag is beneficial when you do not have the required language version of your user’s website, but you want to direct them to your preferred version.
Meta-Content Language Tags
Meta-content language tags help search engines identify your HTML content’s language, however, they are not as specific nor as customizable as hreflang tags.
Using Schema Markup
As mentioned in chapter 4, How to Rank: A Blueprint, schema helps search engines identify useful information for users. You can use schema as a technical signal for international SEO also.
You may use the Google Tag Manager to use schema as a technical signal. Since it is also a ranking factor for Google, it also works in optimizing your website.
Let us move on to geotargeting.
Geotargeting
Geotargeting is the process of delivering differentiated content to visitors based on their geolocation. This becomes your priority once you have put into place all the relevant technical signals for your site. You can assess your website’s performance using Google Analytics. Use Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to identify possible issues with your website as well as to learn its geotargeting potential.
Search Console:
You need to decide on your web structure before you begin the geotargeting process. For instance, if you decide to use ccTLD as your web structure, you can add them to the search console and use the relevant functions based on your ccTLD structure.
You also need to check that your hreflang tags are appropriate and working. Do this by:
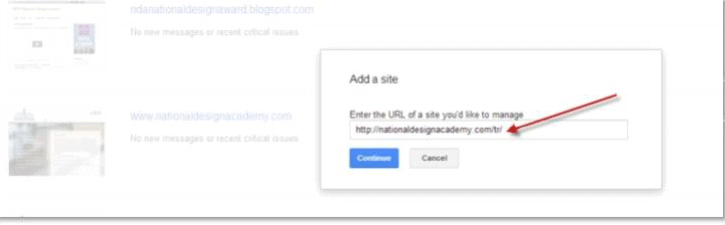
- Ensuring that your country-targeting is correct (If you select ccTLDs as your web structure, it will automatically detect your targeted country).
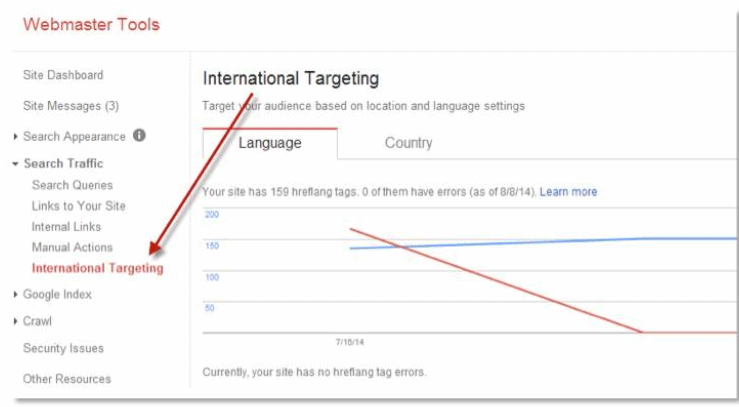
- Performing the same steps on Bing Webmaster Tools.
Now that we have geotargeting in place, let’s learn more about how link-building works for international SEO.
Link-Building for International SEO
Building links is a crucial part of your international SEO process. If you are using ccTLDs or sub-domains as your web structure, you will need it all the more.
Why do you need link-building? Link building is essential as it builds the website’s domain authority and attracts relevant organic traffic. It also helps to improve the website’s searchability. For link building, you need to remember:
- You require a local citation builder.
- You need to do thorough research about your competitors. Once you have information about your competitors, look for websites and influencers you can build a relationship with to help promote your website.
- Utilize tools like BuzzSumo to find trending topics that are relevant to your website.
- You cannot have repetitive content as it does not help with your link-building process. If your content is optimized, you will earn quality links for your website.
- Employ unique strategies in planning for multiple countries. Do not oversimplify the process by using the same method for all regions.
Before we close this chapter, let us look at some tools you can use for the international SEO process.
Tools for International SEO
There are several tools that can help with international SEO. These tools have different functions and can be segregated into categories:
For Researching
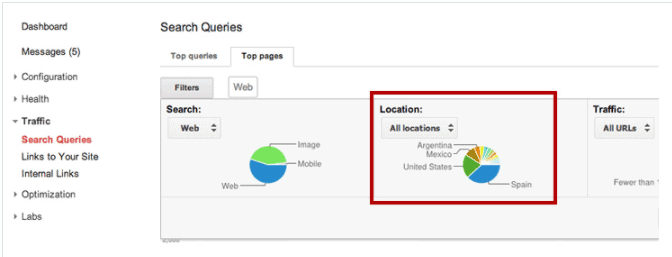
- Google Webmaster Tools. Search Queries helps determine your visibility in international searches.
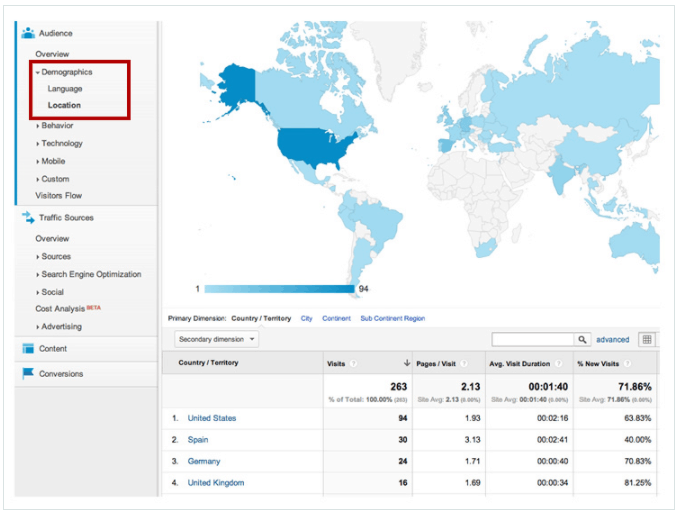
- Google Analytics. Its demographics section can help you understand your current traffic and conversion rate.
- SearchMetrics. It helps you identify your current position relative to your competitors.
- UberSuggest. It helps you identify keywords.
For Targeting
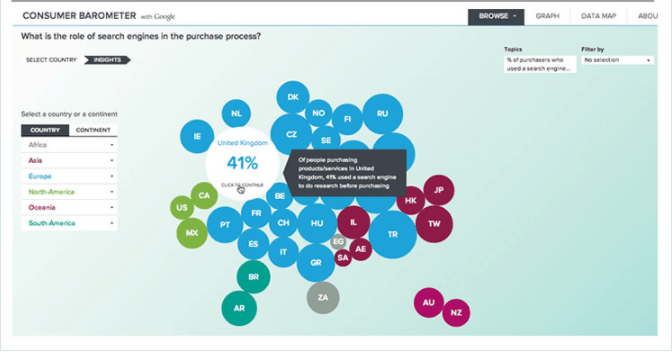
- Google Consumer Barometer. It helps you identify the characteristics of your targeted country or language.
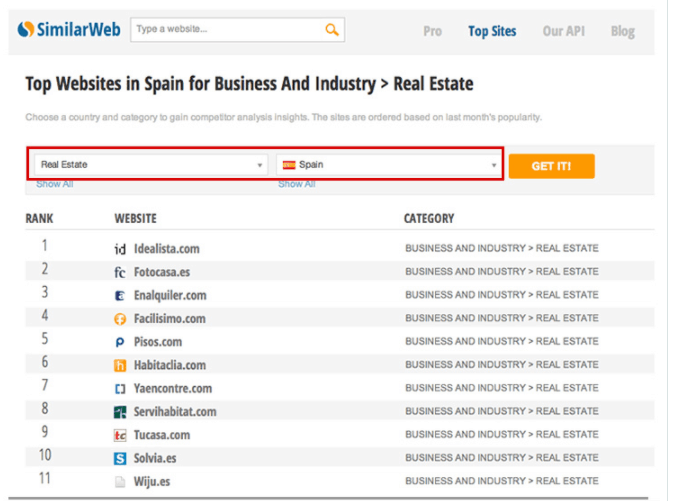
- SimilarWeb. It helps you to understand your competitor’s characteristics and behaviors.
For Optimizing
- DejanSEO Hreflang Validator. It helps you implement the correct hreflang annotations.
- Google Webmaster Tools Geolocation Feature. It helps you geolocate your website if you are targeting a specific country.
- TwitterFall. It helps you follow up on your topics and also helps in geolocation.
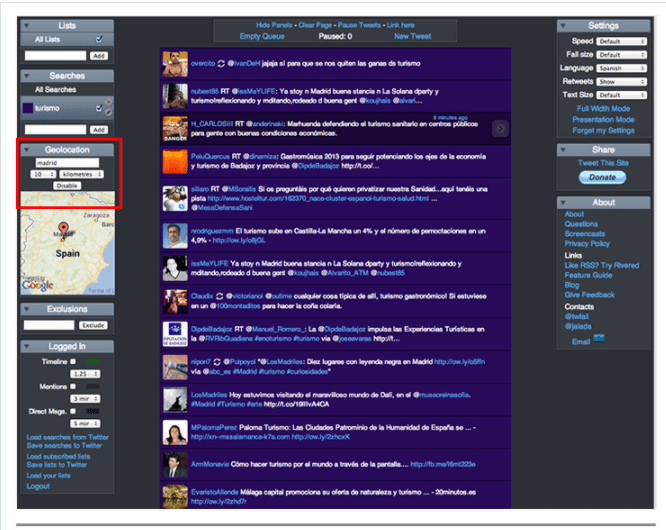
For Promoting
- Open Site Explorer. It helps you understand your competitor’s strategies, sources, and popularity.
- Link Prospector. It helps you promote your website through various factors.
For Measuring
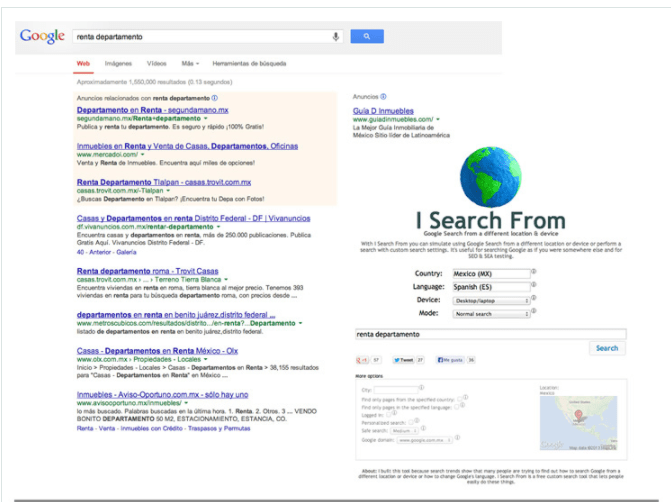
- I Search From. It allows you to simulate a Google search from a different location or device. You can also customize search settings.
- Moz Rank Tracker. It helps you monitor the ranking for each of your web versions.
If you are in charge of an enterprise that is seeking to gain ground in a region, country, set of countries, or perhaps people who speak a certain language, then you will need to make international SEO and its general principles work for you. We hope that this chapter provides you with the foundation you need to do just that.
